Tools
CRISPR Editing Analysis
See Help below on your first use
Help
This program summarize CRISPR editing results based on the idea of CRIS.py. You can read the paper here. The basic idea is summarized in its Fig. 1.
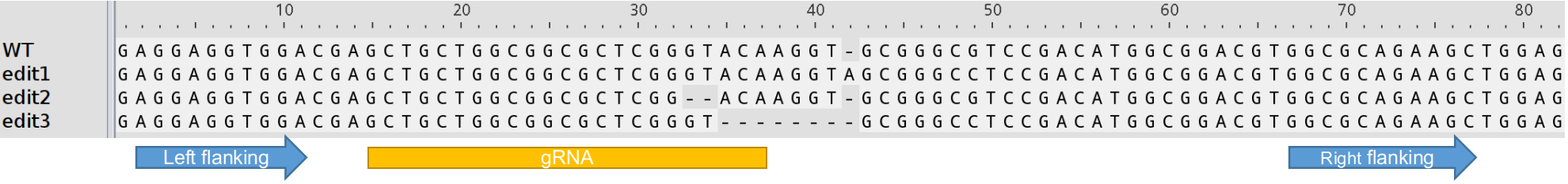
All three sequences (the left and right flanking sequences and the gRNA sequences) should be on the same strand as the template. If you are working on polyploid species, your left or right flanking sequences should be unique to your template (subgenome) if the fastq files include homolog/homeologs.
GitHub page: https://github.com/pinbo/CRISjs
Steps
- Input all the required sequences. Make sure both the left and the right flanking sequences are in the same read or merged read in the fastq file.
- Select fastq or fastq.gz files by clicking “Choose files”.
- Start analyzing by clicking the “Start Analyze” button.
- Download the summary file by clicking the “Download output csv file” button.
You can click the “Example input” button to get the example inputs (then select the example fastq.gz files https://github.com/pinbo/CRISjs/tree/main/example-input).
If you have a lot of fastq files, you may use the standalone command line program CRISgo.
Output
The program will output a csv files reporting the percentage of intact gRNAs (no editing) and percentage of indels. It also gives the sequences and locations of the top 2 mutations and their percentages.
The first line is “Intact reference”: the unedited sequences from the left flanking to the right flanking sequences. The 3rd line is the header of the output table. Explanations here:
fastq_file: the fastq file name
number_of_matched_reads: number of reads that have both flanking sequences
number_of_reads_with_intact_gRNA: matched reads with intact gRNA sequence
%intact_gRNA: % of reads with intact gRNA sequence
total_indel: number of reads with an indel
%indel: %number of reads with an indel
number_of_reads_with_leftSeq: number of reads with the left flanking sequence
number_of_reads_with_rightSeq: number of reads with the right flanking sequence
nleftSeq/nrightSeq: number_of_reads_with_leftSeq / number_of_reads_with_rightSeq
#1_mutation: the most frequenct mutations (SNP or indel)
#1_count: number of reads with #1_mutation
#1_%: #1_count / number_of_matched_reads * 100
#1_seq: the #1 mutation sequence from the left flanking to the right flanking
#1_ref: the reference allele
#1_alt: the mutation allele
#1_bp_left_of_PAM: distance from the PAM sequence
#2_mutation: the 2nd most frequenct mutations (SNP or indel)
#2_count: number of reads with #2_mutation
#2_%: #2_count / number_of_matched_reads * 100
#2_seq: the #2 mutation sequence from the left flanking to the right flanking
#2_ref: the reference allele
#2_alt: the mutation allele
#2_bp_left_of_PAM: distance from the PAM sequence